code:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Sep 5 20:21:03 2024
@author: SavingKing
"""
from pydub import AudioSegment
from pydub.silence import split_on_silence
import os
import time
def mkdir_export(dirname, strr="export"):
dirname_export = os.path.join(dirname, strr)
if not os.path.exists(dirname_export):
os.mkdir(dirname_export)
print(f"已經建立資料夾: {dirname_export}")
else:
print(f"資料夾已經存在: {dirname_export}")
return dirname_export
dirname = r"P:\My Documents\Jeff\錄音\copy\Jeff240606"
basename_wav = "Jeff240606.wav"
path_wav = os.path.join(dirname, basename_wav)
dir_split = mkdir_export(dirname, strr="split")
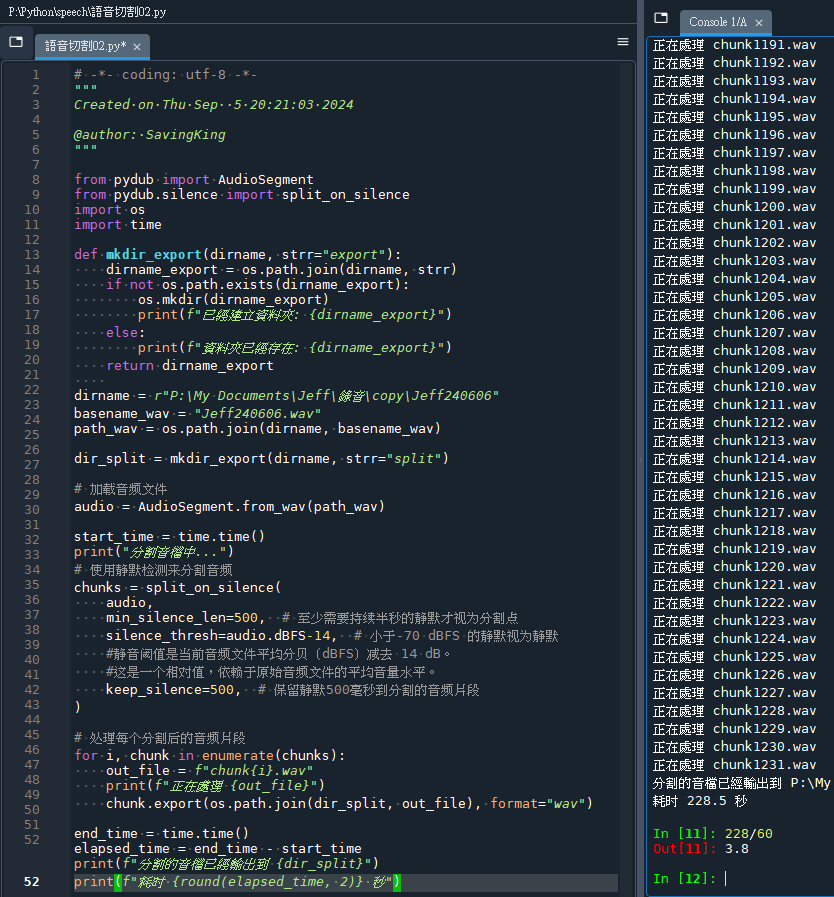
# 加载音频文件
audio = AudioSegment.from_wav(path_wav)
start_time = time.time()
print("分割音檔中...")
# 使用静默检测来分割音频
chunks = split_on_silence(
audio,
min_silence_len=500, # 至少需要持续半秒的静默才视为分割点
silence_thresh=audio.dBFS-14, # 小于-70 dBFS 的静默视为静默
#静音阈值是当前音频文件平均分贝(dBFS)减去 14 dB。
#这是一个相对值,依赖于原始音频文件的平均音量水平。
keep_silence=500, # 保留静默500毫秒到分割的音频片段
)
#type(chunks[0])
#Out[13]: pydub.audio_segment.AudioSegment
basename_main = os.path.splitext(basename_wav)[0]
# 处理每个分割后的音频片段
for i, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
out_file = f"{basename_main}_{i}.wav"
#out_file = f"chunk{i}.wav"
print(f"正在處理 {out_file}")
chunk.export(os.path.join(dir_split, out_file), format="wav")
end_time = time.time()
elapsed_time = end_time - start_time
print(f"分割的音檔已經輸出到 {dir_split}")
print(f"耗时 {round(elapsed_time, 2)} 秒")輸出結果:
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN
![Python: matplotlib如何設定座標軸刻度? plt.xticks(seq, labels) ;如何生成fig, ax物件? fig = plt.figure(figsize= (10.24, 7.68)) ; ax = fig.add_subplot() ; fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10.24, 7.68)) ; 如何使用中文? plt.rcParams[“font.family”] = [“Microsoft JhengHei”] Python: matplotlib如何設定座標軸刻度? plt.xticks(seq, labels) ;如何生成fig, ax物件? fig = plt.figure(figsize= (10.24, 7.68)) ; ax = fig.add_subplot() ; fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10.24, 7.68)) ; 如何使用中文? plt.rcParams[“font.family”] = [“Microsoft JhengHei”]](https://i1.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/20230209083006_41.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)




![Python: 如何使用functools.reduce逐步縮減可迭代對象,合併為單個結果? import functools; product = functools.reduce( lambda x, y: x * y, numbers) ; reduce(function, sequence [, initial]) -> value ; map(function, iterable) ; filter(function, iterable) ; map ; filter Python: 如何使用functools.reduce逐步縮減可迭代對象,合併為單個結果? import functools; product = functools.reduce( lambda x, y: x * y, numbers) ; reduce(function, sequence [, initial]) -> value ; map(function, iterable) ; filter(function, iterable) ; map ; filter](https://i1.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/20230626093403_49.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)

![「Python 的兩條路」:一次搞懂 sys.path (找 .py) 與 os.environ[‘PATH’] (找 .exe) 的愛恨情仇 「Python 的兩條路」:一次搞懂 sys.path (找 .py) 與 os.environ[‘PATH’] (找 .exe) 的愛恨情仇](https://i0.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/20260114094100_0_424ead.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)


近期留言