
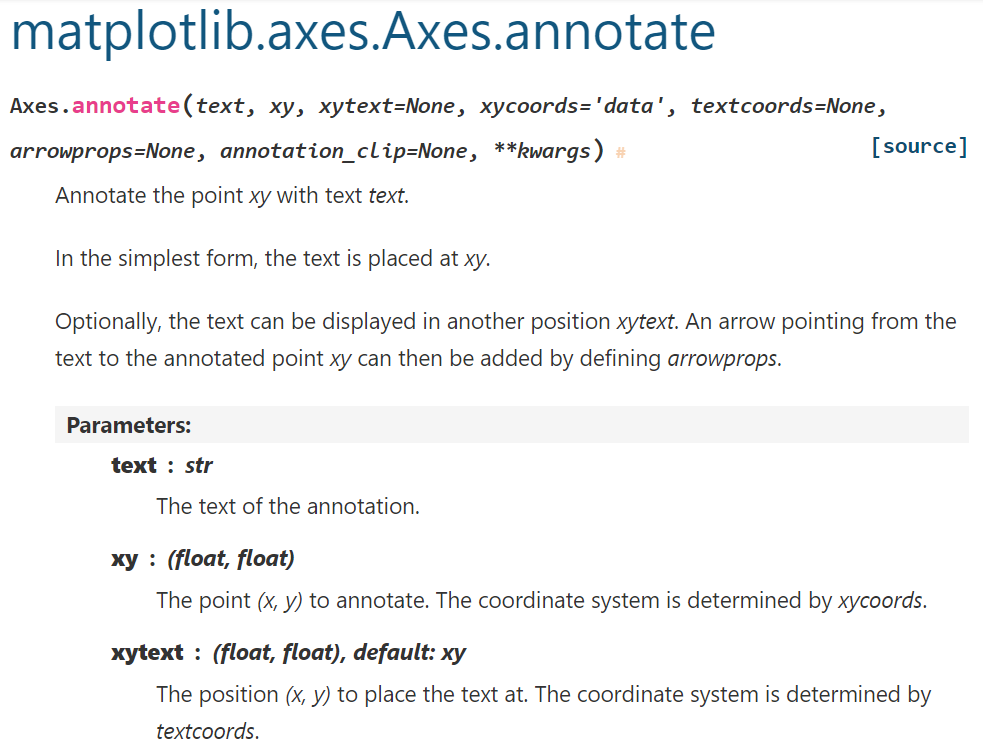
一看就知道ax.annotate() 比 ax.text() 多很多參數
code:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 创建数据
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
# 绘制图像
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y, 'b-', label='sin(x)')
ax.legend()
# 标注数据点
index_max = np.argmax(y)
x_max = x[index_max]
y_max = y[index_max]
# 使用plt.text()进行标注
ax.text(x_max, y_max, f'max value={y_max:.2f}',
fontsize=12, ha='left', va='top', color='r')
# 使用plt.annotate()进行标注
ax.annotate(f'max value={y_max:.2f}',
xy=(x_max, y_max),
xytext=(x_max-0.5, y_max-0.5),
fontsize=12,
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->',
connectionstyle='arc3',
color='k'))
plt.show()plt.text()和plt.annotate()都是在matplotlib中用於在圖表上添加文字標籤的方法,它們的區別在於:
plt.text()可以在圖表的任何位置添加文本,而且位置是通過x和y座標指定的,它不會參考到圖表中的任何其他對象。plt.annotate()則允許您參考圖表中的其他對象,例如數據點或軸線,以便在這些對象上添加標籤。annotate()通常用於在圖表上標記特定點或添加標籤箭頭,因為它具有自動計算位置和對齊文本的功能。
簡而言之,如果您只是想在圖表上添加一些簡單的文字,則可以使用plt.text(),但如果您需要參考圖表中的其他對象或添加箭頭,則應使用plt.annotate()。
ax.text()中的ha va 參數:
horizontalalignment or ha | {‘left’, ‘center’, ‘right’} |
“right”資料點在說明文字的右邊
“center”(中心) 依此類推
#不是”middle”(中間)
verticalalignment or va | {‘bottom’, ‘baseline’, ‘center’, ‘center_baseline’, ‘top’} |
輸出結果:

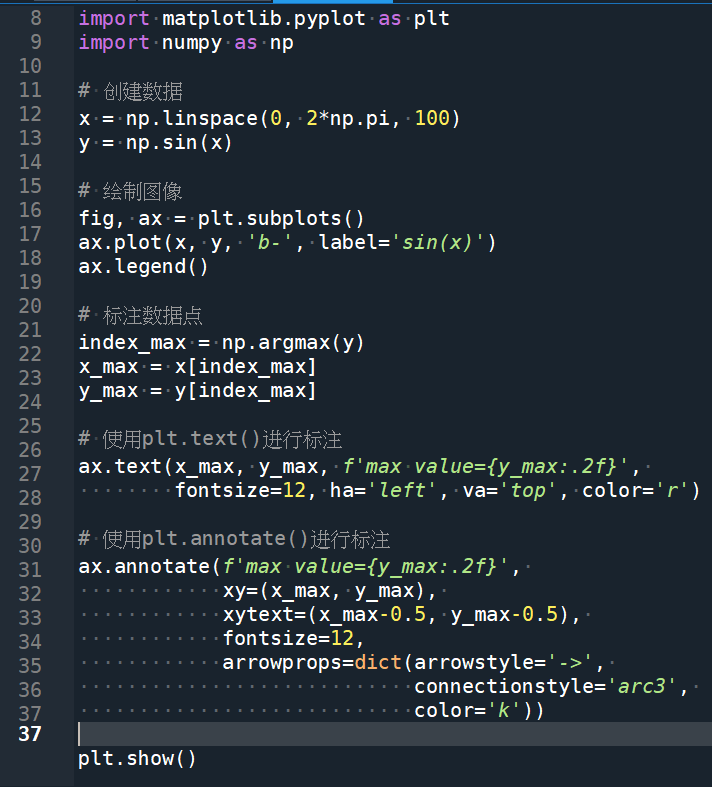
可以看到,两者最大的区别是 plt.annotate() 可以添加箭头,并且可以指定箭头的样式、颜色等属性,从而更清晰地指出注释的方向和目标。此外,plt.annotate() 还可以更好地控制注释的位置和对齐方式。
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN
ax.annotate("max-3dB", xy=(theta_max, target),
xytext=(theta_max - 0.5, target - 5),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', arrowstyle='->'),
fontsize=fontsz, ha="center")輸出結果:
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN







![Python網路爬蟲requests 如何下載台灣證交所的opendata? rawData = requests. get (inputs) #<Response [200]> Python網路爬蟲requests 如何下載台灣證交所的opendata? rawData = requests. get (inputs) #<Response [200]>](https://i1.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/20221004135740_43.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)

![Python TQC 510 費氏數列,list[], f.append(n3) - 儲蓄保險王](https://savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/20220522152013_66-520x245.jpg)
近期留言