1. 安裝套件
確保你已經安裝最新版 openai:
pip install --upgrade openai2. 初始化 AsyncAzureOpenAI
在 Azure OpenAI,你需要設定:
api_key:Azure OpenAI 的金鑰azure_endpoint:Azure OpenAI 的服務端點 URLapi_version:API 版本(通常是"2024-05-01-preview"或更新版本)model:你在 Azure 部署的模型名稱(例如"gpt-4o","gpt-4.1")
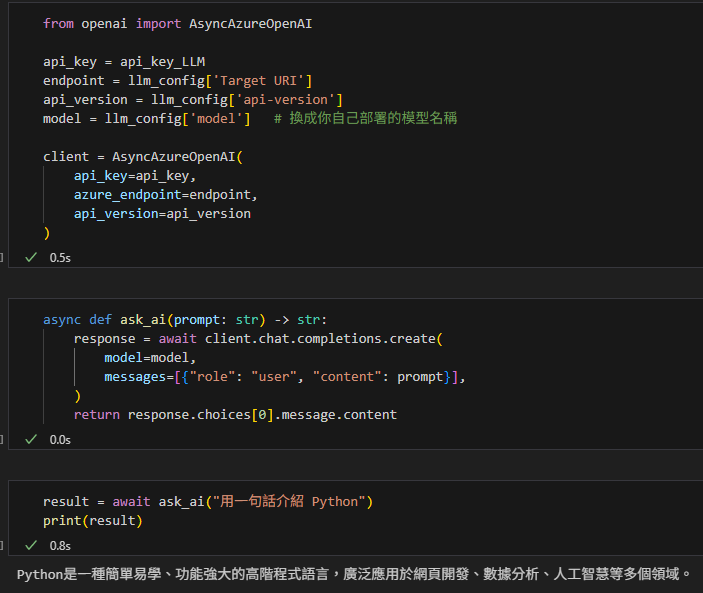
from openai import AsyncAzureOpenAI
api_key = "你的金鑰"
endpoint = "https://你的資源名稱.openai.azure.com/"
api_version = "2024-05-01-preview"
model = "gpt-4o" # 換成你自己部署的模型名稱
client = AsyncAzureOpenAI(
api_key=api_key,
azure_endpoint=endpoint,
api_version=api_version
)3. 建立一個簡單的非同步函式
這個函式會把使用者輸入丟到模型,並回傳文字
async def ask_ai(prompt: str) -> str:
response = await client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
)
return response.choices[0].message.content4. 在 Jupyter Notebook 測試單次呼叫
Jupyter 已經有 event loop,所以直接用 await:
result = await ask_ai("用一句話介紹 Python")
print(result)輸出應該會是類似:
5. 並行呼叫(同時送出多個請求)
如果你要同時問兩個問題,可以用 asyncio.gather:
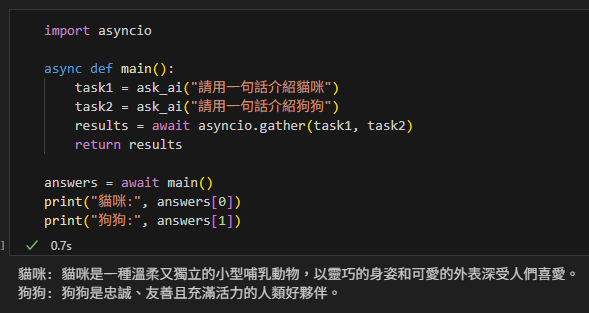
import asyncio
async def main():
task1 = ask_ai("請用一句話介紹貓咪")
task2 = ask_ai("請用一句話介紹狗狗")
results = await asyncio.gather(task1, task2)
return results
answers = await main()
print("貓咪:", answers[0])
print("狗狗:", answers[1])這時候兩個請求會 同時送出,總時間會接近「最慢的那一個」,而不是兩個加總。
🎯 總結
- 初始化 client → 用
AsyncAzureOpenAI - 呼叫 API → 用
await client.chat.completions.create(...) - 取文字 →
response.choices[0].message.content - Jupyter Notebook → 直接
await,不用asyncio.run() - 並行呼叫 → 用
asyncio.gather()
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN
使用同步client + threading:
from openai import OpenAI, AzureOpenAI
client_LLM = AzureOpenAI(
api_key=api_key_LLM,
azure_endpoint=endpoint_LLM,
api_version=api_version_LLM)
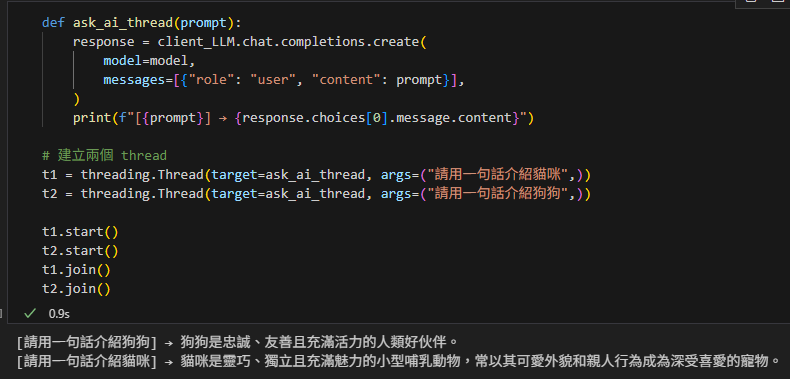
def ask_ai_thread(prompt):
response = client_LLM.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
)
print(f"[{prompt}] → {response.choices[0].message.content}")
# 建立兩個 thread
t1 = threading.Thread(target=ask_ai_thread, args=("請用一句話介紹貓咪",))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=ask_ai_thread, args=("請用一句話介紹狗狗",))
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()輸出結果:
1. 共同點:都能「同時」呼叫 API
原因很簡單:
- API 呼叫是 I/O 密集型工作(等待網路回覆)。
- 不管是 threading 還是 asyncio,都能在等待期間「不要卡住主程式」,所以看起來能同時發多個請求。
2. 差異:執行方式不同
🔹 Threading
- 真的開多個 作業系統層級的 thread。
- 每個 thread 都在跑「同步 client」,互相獨立。
- 如果你開 100 個請求,就會開 100 個 thread,開銷大(記憶體、切換成本)。
👉 適合:你已經有同步 client,不想改程式架構,直接用 thread 包起來就能並行。
🔹 Asyncio
- 單一 thread,靠事件迴圈(event loop)管理 coroutine。
- API 呼叫時,程式會「掛起等待」,事件迴圈可以去處理其他任務。
- 不需要真的開 100 個 thread,只要一個 event loop,就能處理成千上萬個 I/O。
👉 適合:大量 API 請求、伺服器程式,對效能和資源使用比較友善。
3. 類比解釋 🚌 vs 🚕
- Threading = 一人一台計程車 → 每個請求都有獨立的車(thread),互不干擾,但油耗大、維護貴。
- Asyncio = 一台公車 → 大家共用一台車(event loop),司機(事件迴圈)很聰明,能在不同乘客下車的空檔去接別人。效率高,但規則比較嚴格(要用
await)。
4. 為什麼兩種都能做?
因為任務屬於「I/O-bound」(等待網路),
- threading 讓多個請求同時發出去 → OK ✅
- asyncio 讓單一事件迴圈同時管理多個請求 → 也 OK ✅
所以兩種都能達成「同時呼叫 API」的效果。
🎯 總結
- Threading:簡單粗暴,適合同步 client,缺點是 thread 開銷大。
- Asyncio:更輕量,適合大量 API 呼叫,但要用 async client +
await。 - 在小規模測試時,兩種看起來差不多;但在大規模請求(例如 1000 個 API call)時,asyncio 的效能會明顯更好。
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN
比較完全同步 (逐一呼叫)
Threading 版本
Asyncio 版本
import time
import threading
import asyncio
from openai import AzureOpenAI, AsyncAzureOpenAI
# ========= 建立同步 client =========
if config["Azure_LLM"]:
llm_config = dic_api_key['AzureOpenAI_gpt-4.1']
model_LLM = llm_config['model']
endpoint_LLM = llm_config['Target URI']
api_key_LLM = llm_config['api_key']
api_version_LLM = llm_config['api-version']
client_LLM_sync = AzureOpenAI(
api_key=api_key_LLM,
azure_endpoint=endpoint_LLM,
api_version=api_version_LLM
)
client_LLM_async = AsyncAzureOpenAI(
api_key=api_key_LLM,
azure_endpoint=endpoint_LLM,
api_version=api_version_LLM
)
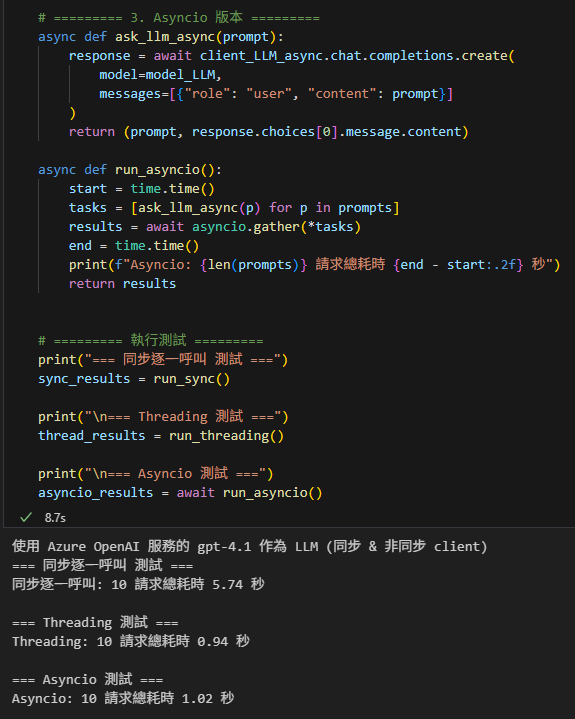
print(f"使用 Azure OpenAI 服務的 {model_LLM} 作為 LLM (同步 & 非同步 client)")
# 測試輸入資料 (模擬 10 個問題)
prompts = [f"請用一句話介紹動物 {i}" for i in range(10)]
# ========= 1. 完全同步 (逐一呼叫) =========
def run_sync():
results = []
start = time.time()
for p in prompts:
response = client_LLM_sync.chat.completions.create(
model=model_LLM,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": p}]
)
results.append((p, response.choices[0].message.content))
end = time.time()
print(f"同步逐一呼叫: {len(prompts)} 請求總耗時 {end - start:.2f} 秒")
return results
# ========= 2. Threading 版本 =========
def ask_llm_thread(prompt, results):
response = client_LLM_sync.chat.completions.create(
model=model_LLM,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
results.append((prompt, response.choices[0].message.content))
def run_threading():
threads = []
results = []
start = time.time()
for p in prompts:
th = threading.Thread(target=ask_llm_thread, args=(p, results))
threads.append(th)
th.start()
for th in threads:
th.join()
end = time.time()
print(f"Threading: {len(prompts)} 請求總耗時 {end - start:.2f} 秒")
return results
# ========= 3. Asyncio 版本 =========
async def ask_llm_async(prompt):
response = await client_LLM_async.chat.completions.create(
model=model_LLM,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
return (prompt, response.choices[0].message.content)
async def run_asyncio():
start = time.time()
tasks = [ask_llm_async(p) for p in prompts]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
end = time.time()
print(f"Asyncio: {len(prompts)} 請求總耗時 {end - start:.2f} 秒")
return results
# ========= 執行測試 =========
print("=== 同步逐一呼叫 測試 ===")
sync_results = run_sync()
print("\n=== Threading 測試 ===")
thread_results = run_threading()
print("\n=== Asyncio 測試 ===")
asyncio_results = await run_asyncio()輸出:
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN









近期留言