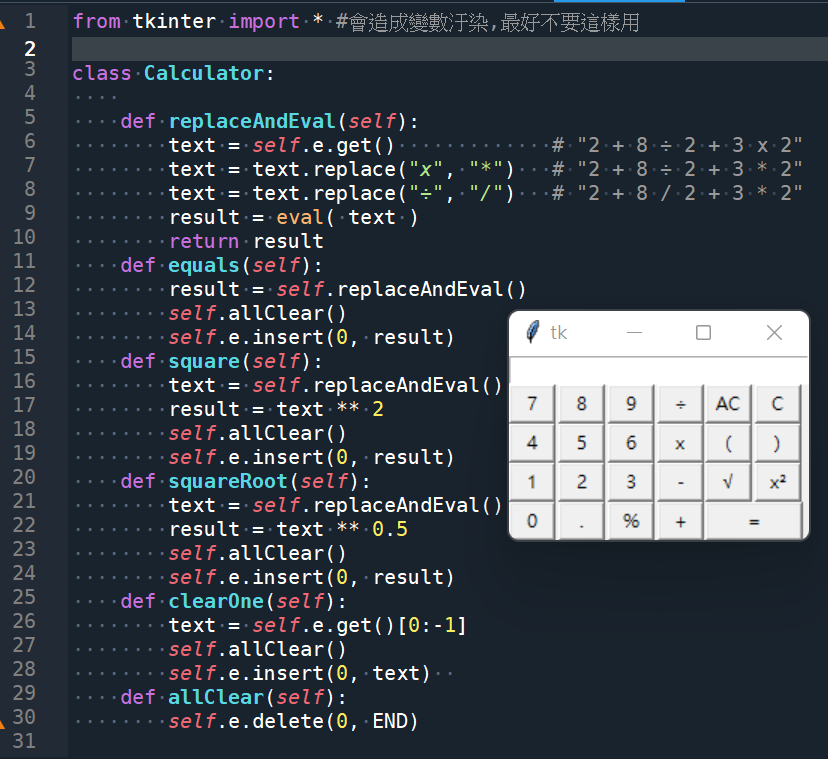
from tkinter import * #會造成變數汙染,最好不要這樣用
class Calculator:
def replaceAndEval(self):
text = self.e.get() # “2 + 8 ÷ 2 + 3 x 2”
text = text.replace(“x”, “*”) # “2 + 8 ÷ 2 + 3 * 2”
text = text.replace(“÷”, “/”) # “2 + 8 / 2 + 3 * 2”
result = eval( text )
return result
def equals(self):
result = self.replaceAndEval()
self.allClear()
self.e.insert(0, result)
def square(self):
text = self.replaceAndEval()
result = text ** 2
self.allClear()
self.e.insert(0, result)
def squareRoot(self):
text = self.replaceAndEval()
result = text ** 0.5
self.allClear()
self.e.insert(0, result)
def clearOne(self):
text = self.e.get()[0:-1]
self.allClear()
self.e.insert(0, text)
def allClear(self):
self.e.delete(0, END)
def enterChar(self, symbol):
self.e.insert(END, symbol)
def __init__(self, window):
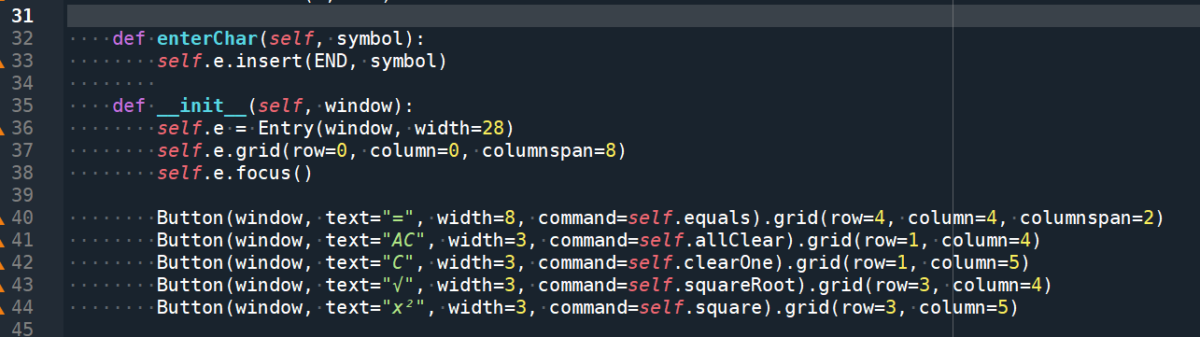
“”” 參數window只在__init__()
這個function使用到,
沒有使用self.window承接這個參數
__init__() 的縮排內,
就可以只寫window
不用寫self.window
但若class內的其他function
也要用window這個參數
這種寫法就不一定方便,
要把window也傳去別的function “””
self.e = Entry(window, width=28)
self.e.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=8)
self.e.focus()
Button(window, text=”=”, width=8, command=self.equals).grid(row=4, column=4, columnspan=2)
Button(window, text=”AC”, width=3, command=self.allClear).grid(row=1, column=4)
Button(window, text=”C”, width=3, command=self.clearOne).grid(row=1, column=5)
Button(window, text=”√”, width=3, command=self.squareRoot).grid(row=3, column=4)
Button(window, text=”x²”, width=3, command=self.square).grid(row=3, column=5)
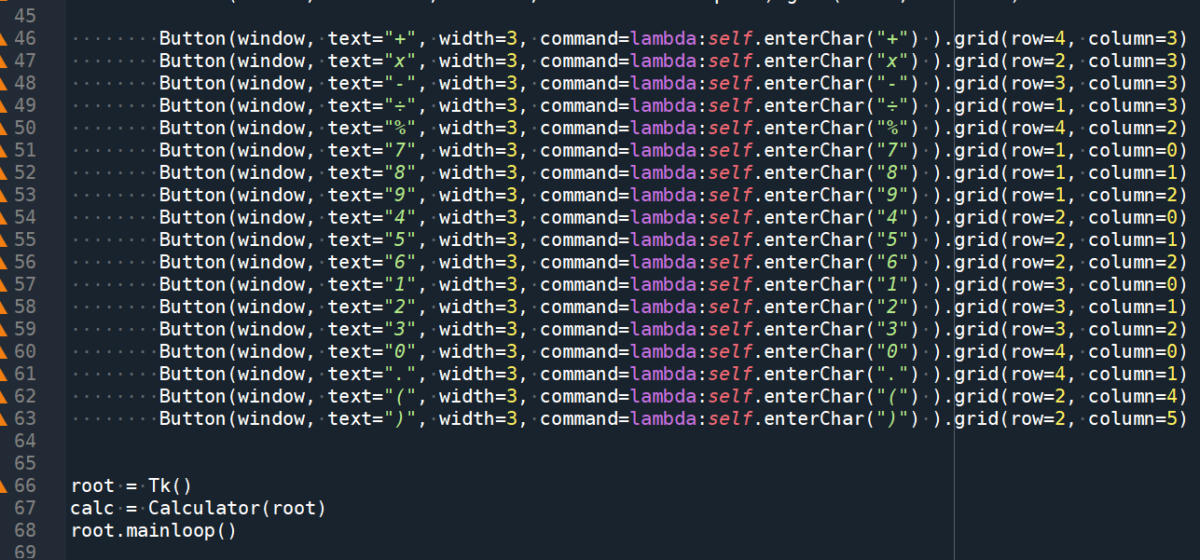
Button(window, text=”+”, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“+”) ).grid(row=4, column=3)
Button(window, text=”x”, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“x”) ).grid(row=2, column=3)
Button(window, text=”-“, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“-“) ).grid(row=3, column=3)
Button(window, text=”÷”, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“÷”) ).grid(row=1, column=3)
Button(window, text=”%”, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“%”) ).grid(row=4, column=2)
Button(window, text=”7″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“7”) ).grid(row=1, column=0)
Button(window, text=”8″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“8”) ).grid(row=1, column=1)
Button(window, text=”9″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“9”) ).grid(row=1, column=2)
Button(window, text=”4″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“4”) ).grid(row=2, column=0)
Button(window, text=”5″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“5”) ).grid(row=2, column=1)
Button(window, text=”6″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“6”) ).grid(row=2, column=2)
Button(window, text=”1″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“1”) ).grid(row=3, column=0)
Button(window, text=”2″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“2”) ).grid(row=3, column=1)
Button(window, text=”3″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“3”) ).grid(row=3, column=2)
Button(window, text=”0″, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“0”) ).grid(row=4, column=0)
Button(window, text=”.”, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“.”) ).grid(row=4, column=1)
Button(window, text=”(“, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“(“) ).grid(row=2, column=4)
Button(window, text=”)”, width=3, command=lambda:self.enterChar(“)”) ).grid(row=2, column=5)
root = Tk()
calc = Calculator(root)
root.mainloop()
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN
![Python Pathlib 實戰:優雅地篩選多種圖片檔案; images = [f for f in p.glob(“*”) if f.suffix.lower() in img_extensions] Python Pathlib 實戰:優雅地篩選多種圖片檔案; images = [f for f in p.glob(“*”) if f.suffix.lower() in img_extensions]](https://i0.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/20260128111659_0_736612.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)



![Python-docx 圖片提取完全指南:從 rId 到二進位資料的探險rid ; part = doc.part.rels[rid].target_part #return part.blob if “ImagePart” in type(part).__name__ else None Python-docx 圖片提取完全指南:從 rId 到二進位資料的探險rid ; part = doc.part.rels[rid].target_part #return part.blob if “ImagePart” in type(part).__name__ else None](https://i0.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/20260113135812_0_8fa645.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)

![Python 如何用pandas.Series.nsmallest() 找到n個與target差距最小的index?再從中找到距離idxmax最近的index?避免誤抓sidelobes的index? targetIdx = (serMean-target_value).abs().nsmallest(n).index.tolist() ;Series切片: .loc[標籤名1:標籤名2] (會含標籤名2) ; .iloc[位置1:位置2] (不含位置2) Python 如何用pandas.Series.nsmallest() 找到n個與target差距最小的index?再從中找到距離idxmax最近的index?避免誤抓sidelobes的index? targetIdx = (serMean-target_value).abs().nsmallest(n).index.tolist() ;Series切片: .loc[標籤名1:標籤名2] (會含標籤名2) ; .iloc[位置1:位置2] (不含位置2)](https://i0.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/20230222082954_53.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)


近期留言