code:
import json
import os
dirname = r"D:\json"
basename = "test_json_comment.json"
fpath = os.path.join(dirname, basename)
with open( fpath , encoding="UTF-8" ) as json_file:
dic = json.load(json_file)
json_file.seek(0,0)
strr = json_file.read()
print("strr:",strr)
dic1 = json.loads(strr)
print("\ndic:",dic)
print("\ndic1",dic1)輸出結果:
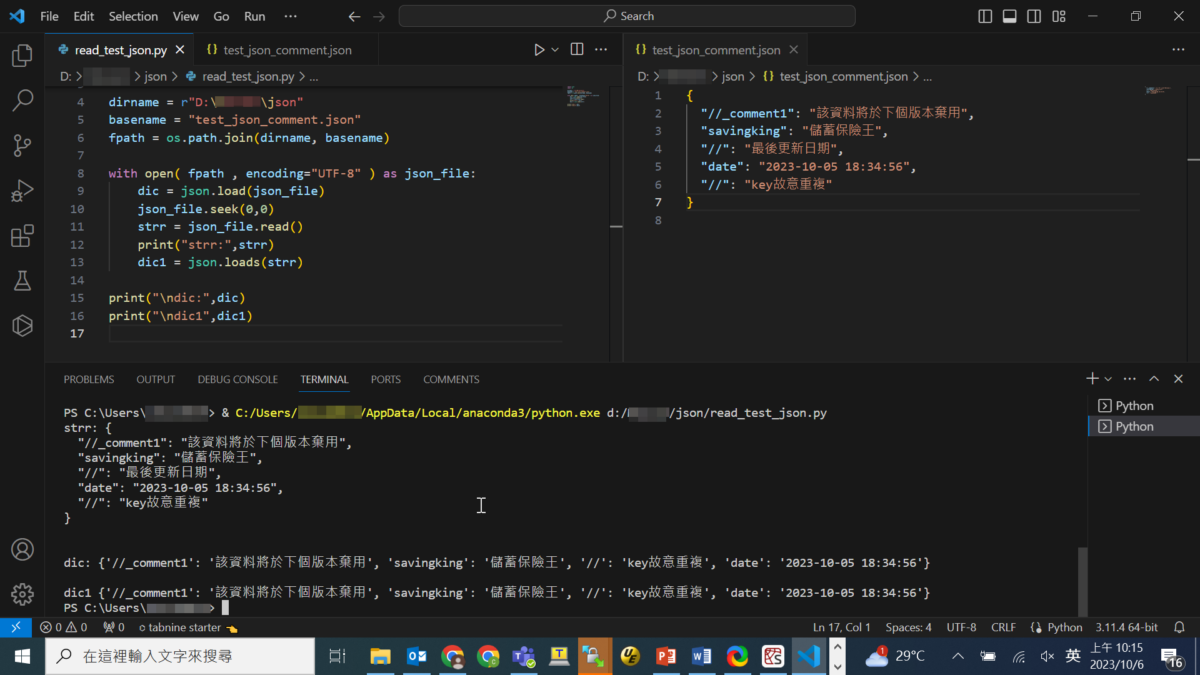
json.load 方法用於從文件中讀取並解析JSON數據,然後將其轉換為Python數據結構(字典、列表等)。在代碼中,已經使用了 json.load 來加載數據,並將其存儲在了 dic 變量中,因此不需要再次使用 json_file.read() 來讀取JSON文件的內容。
一旦使用 json.load 方法讀取了JSON文件的內容,文件指針就會在文件的末尾,若沒有json_file.seek(0,0)跳回文件的一開頭,再次調用 json_file.read() 將返回空字符串,因為已經到達了文件的末尾。
json.load(json_file) 跟
json.loads(strr)
參數的型別不一樣:
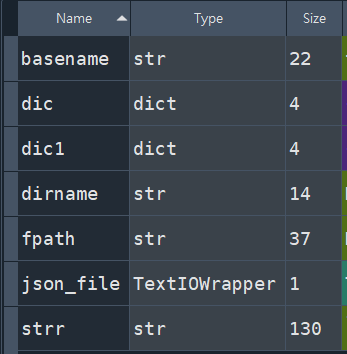
json_file.seek(0,0)
#第一個0表示文件之開頭
#第二個0表示偏移0
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN









![Python: 如何使用pandas.to_numeric ( df['numbers'], errors='coerce') 將非數值型資料轉為NaN? df['numbers'].describe() 簡述統計資料 - 儲蓄保險王](https://savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/20240501052102_0-520x245.png)
近期留言