MSE(mean_squared_error):
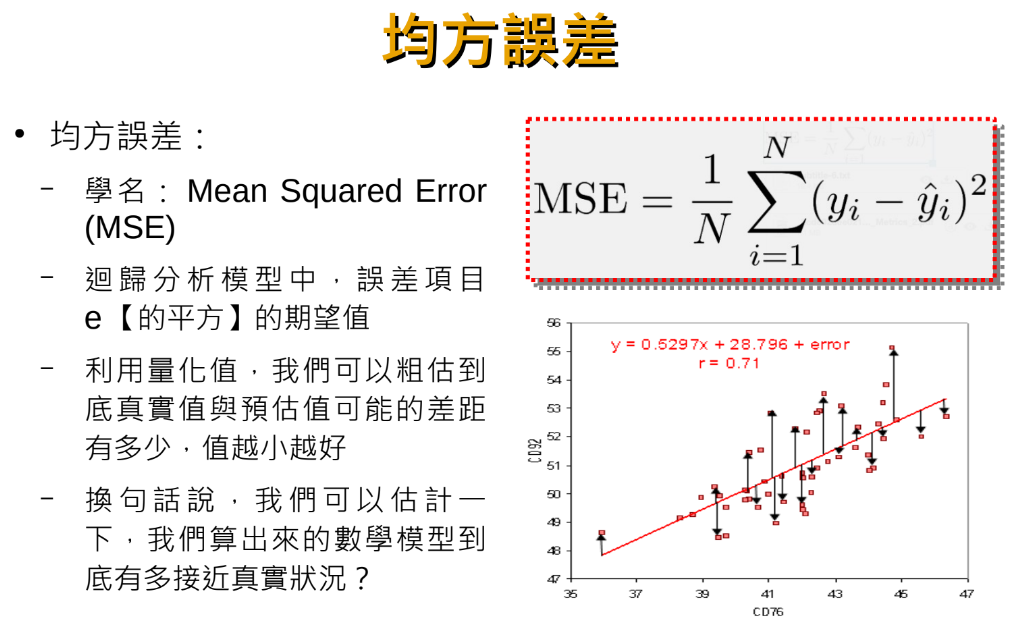
from sklearn import linear_model,metrics #指標
mse = metrics.mean_squared_error(ytest,ypredict)
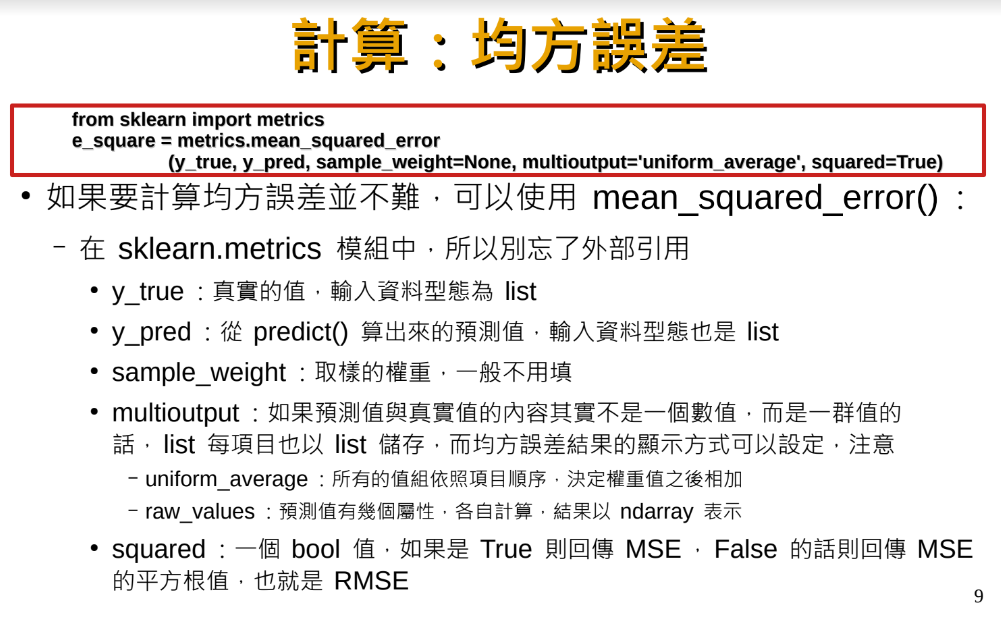
判定係數(R-squared):
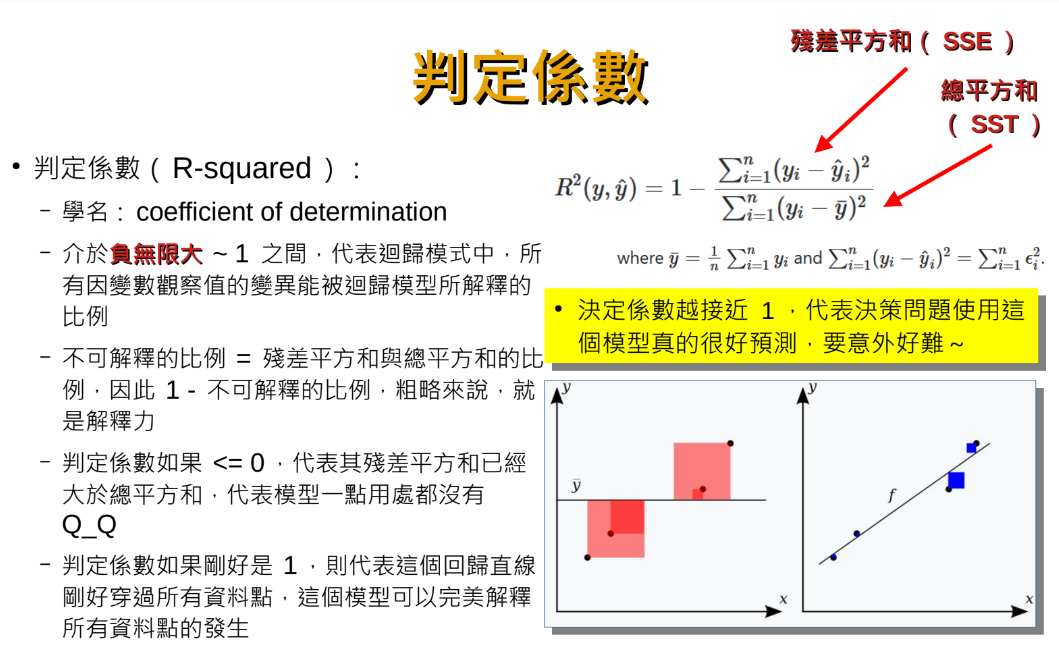
y^: 預測值
y bar: 平均值
計算判定係數(R-squared):

皮爾森積差相關係數
(Pearson correlation coefficient):
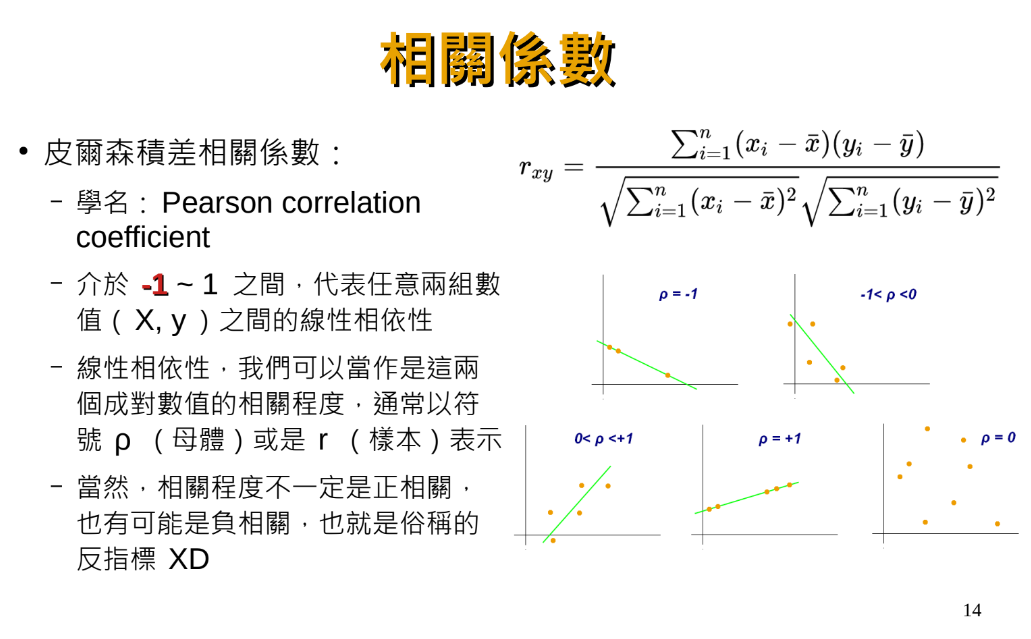
計算皮爾森積差相關係數:

多維度線性迴歸:

from sklearn import linear_model,metrics
import pandas as pd
import sys
fpath = r”C:\Python\P107\doc\BostonHousing.csv”
dataset = pd.read_csv(fpath) #.shape = (506, 14)
headerList = dataset.columns.tolist()
cols = dataset.columns.size
# dataset.columns.size = 14
# ==================================================
# x = dataset.drop(headerList[-1],axis=1).values #(506, 13)
# y = dataset[headerList[-1]].values #(506,)
# ==================================================
x=dataset.iloc[:,0:cols-1].values #(506, 13)
y=dataset.iloc[:,cols-1:].values.ravel() #(506,)
#沒有ravel()的話,(506,1) 多出一個維度,第二維長度僅有1
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
xtrain,xtest,ytrain,ytest =\
train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.3,
random_state=42,shuffle=True)
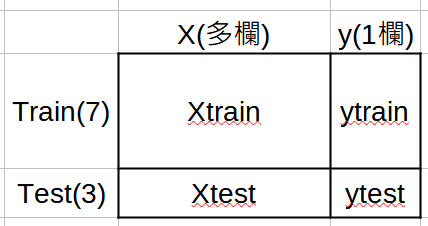
# 1. train_test_split()將原始資料切割為
# xtrain, xtest, ytrain, ytest
# =============================================
# print(“The shpae of training data(X axis):”,xtrain.shape)
# print(“The shpae of training data(Y axis):”,ytrain.shape)
# print(“The shpae of testing data(X axis):”,xtest.shape)
# print(“The shpae of testing data(Y axis):”,ytest.shape)
# ==============================================
regr_train = linear_model.LinearRegression()
#2. 建立LinearRegression操作子
regr_train.fit(xtrain,ytrain)
#3. 用. fit(xtrain, ytrain) 影響操作子
ypredict = regr_train.predict(xtest)
#4. 用.predict(xtest) 生出預測值ypredict
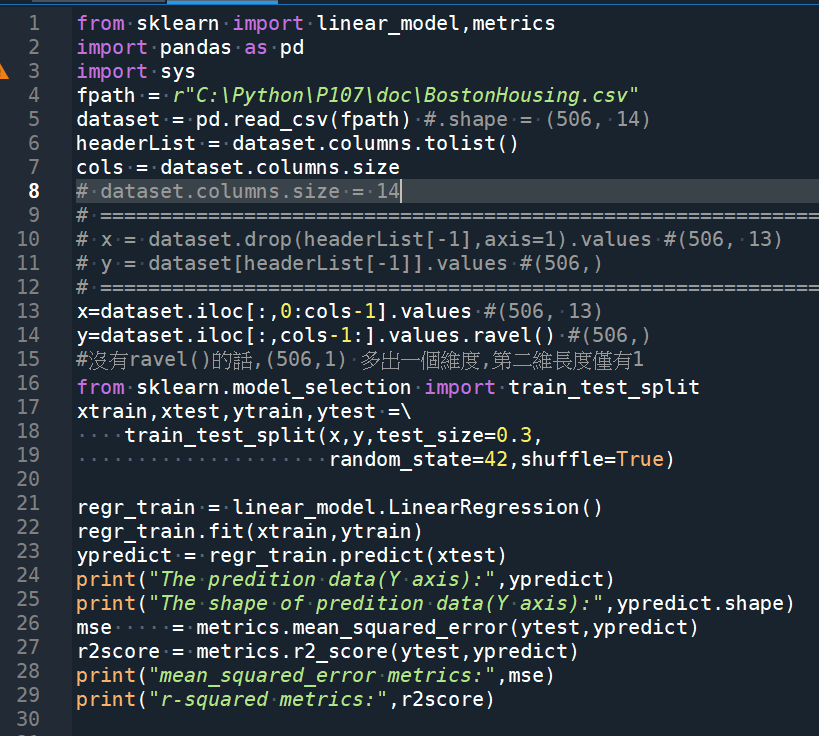
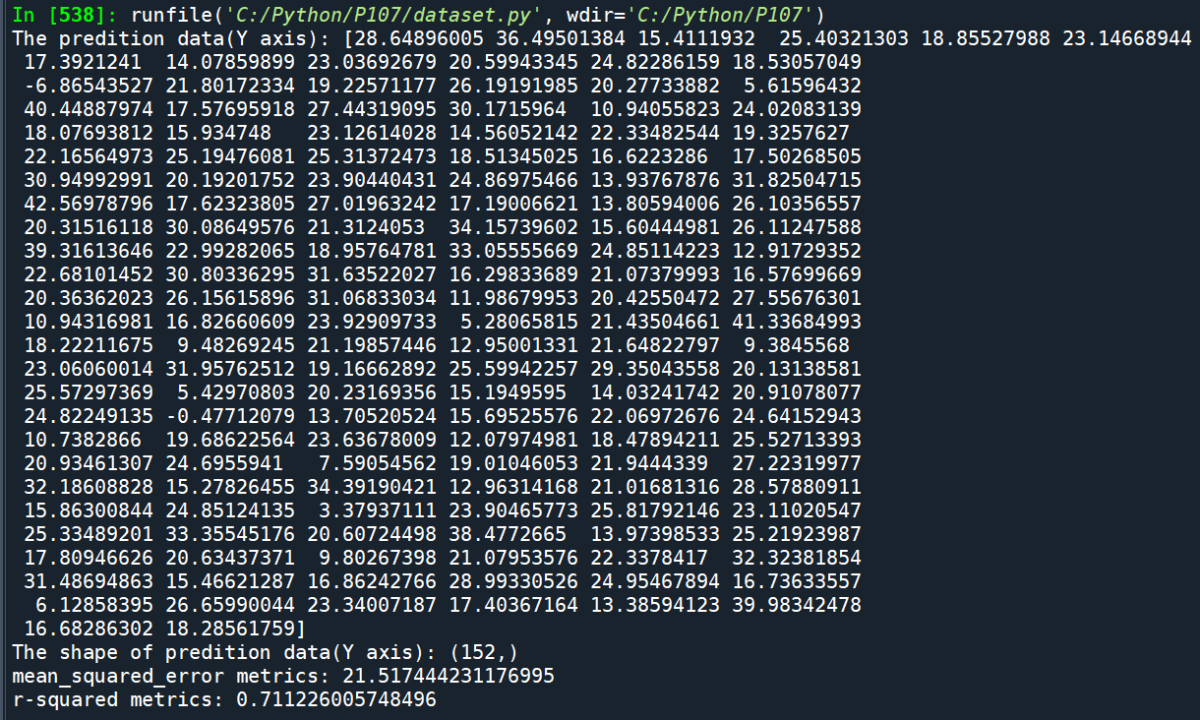
print(“The predition data(Y axis):”,ypredict)
print(“The shape of predition data(Y axis):”,ypredict.shape)
mse = metrics.mean_squared_error(ytest,ypredict)
r2score = metrics.r2_score(ytest,ypredict)
# 5. ytest是真實資料,ypredict是預測值,
#有這兩者就可以用來計算mse跟r2_score
print(“mean_squared_error metrics:”,mse)
print(“r-squared metrics:”,r2score)
輸出結果:
p value:

推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN

![Python TQC 510 費氏數列,list[], f.append(n3) Python TQC 510 費氏數列,list[], f.append(n3)](https://i0.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/20220522152013_66.jpg?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)





![Python: 如何使用numpy.newaxis 增加資料的維度? y = x[:, np.newaxis] Python: 如何使用numpy.newaxis 增加資料的維度? y = x[:, np.newaxis]](https://i2.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/20230313184351_57.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)
![Python 進階實戰:深入 Word 核心,挖出那一坨 BLOB (含自省 Debug 技巧, BLOB= Binary Large Object) ; part = doc.part.rels[rid].target_part ; return part.blob if “ImagePart” in type(part).__name__ else None Python 進階實戰:深入 Word 核心,挖出那一坨 BLOB (含自省 Debug 技巧, BLOB= Binary Large Object) ; part = doc.part.rels[rid].target_part ; return part.blob if “ImagePart” in type(part).__name__ else None](https://i1.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/20260126111046_0_cd8751.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)
![Python: Regular Expression 正規表示法 正則表達式 import re ; pattn = "[d]{4}/[01][d]/[0123][d] [d]{6}" ; match = re .search (pattn,text) .group() - 儲蓄保險王](https://savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/20220901154435_19-520x245.png)
近期留言