import numpy as np
# 一维数组
a = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(a[..., 1]) # 等同于 a[1],输出:2
# 二维数组
b = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
print(b[..., 1]) # 等同于 b[:, 1],输出:[2 4 6]
print(b[1, ...]) # 等同于 b[1, :],输出:[3 4]
# 三维数组
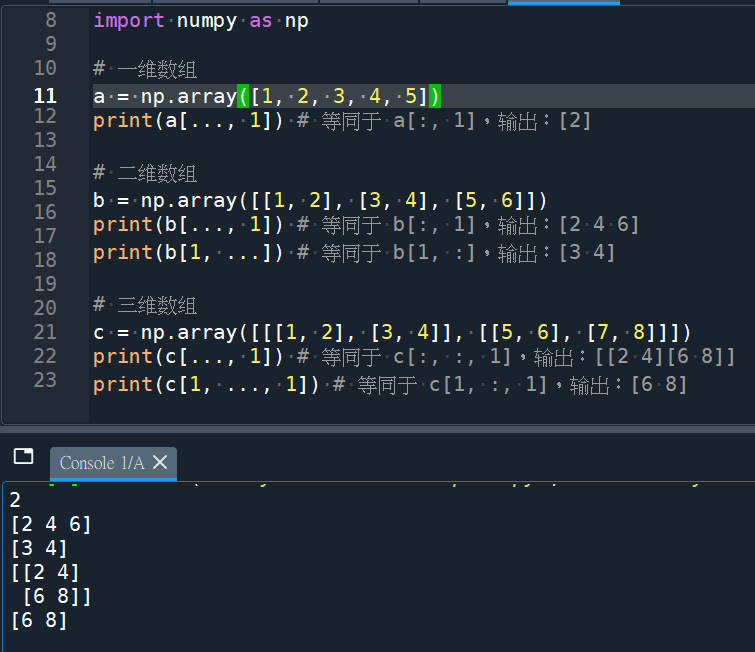
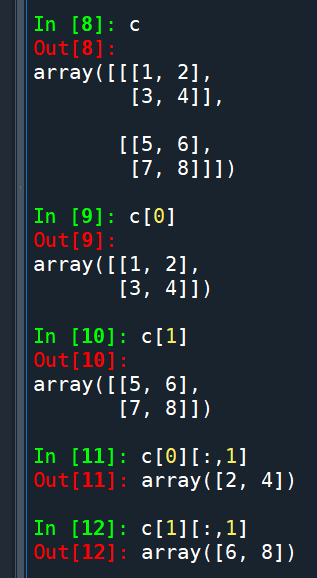
c = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]])
print(c[..., 1]) # 等同于 c[:, :, 1],输出:[[2 4][6 8]]
print(c[1, ..., 1]) # 等同于 c[1, :, 1],输出:[6 8]
print(c[…, 1]) # 等同于 c[:, :, 1],输出:[[2 4][6 8]]:
推薦hahow線上學習python: https://igrape.net/30afN


![Python TQC考題404 數字反轉判斷,n_rev=n[::-1], list1.reverse() Python TQC考題404 數字反轉判斷,n_rev=n[::-1], list1.reverse()](https://i1.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/20220825152414_97.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)







近期留言