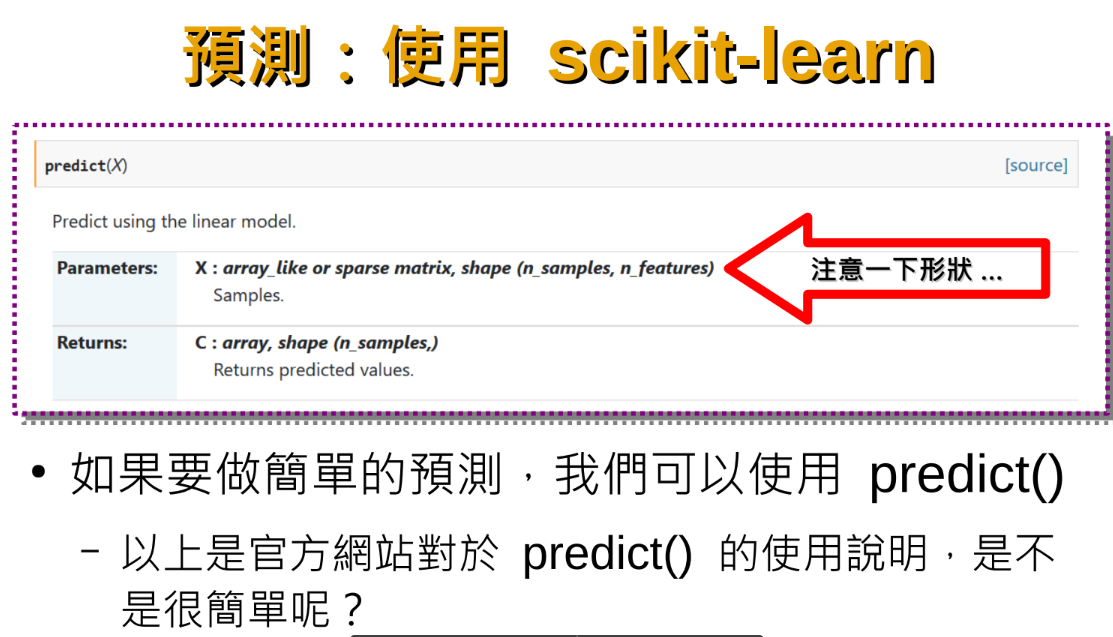
from sklearn import linear_model
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression(*,)
#產生regr操作子,可命名為lmLR
*右方的參數,
表示要連名帶姓寫出參數名稱
依順序寫不行

regr.fit(x,y)
#直接對操作子regr產生影響

regr.coef_ #係數
regr.intercept_ #截距

pred = regr.predict([[40],[5],[15]]) #注意shape
regression:
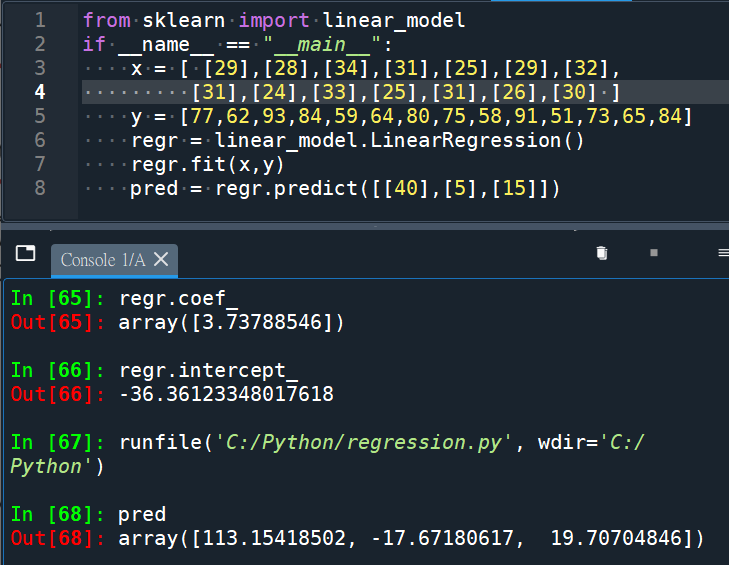
from sklearn import linear_model
if __name__ == “__main__”:
x = [ [29],[28],[34],[31],[25],[29],[32],[31],[24],[33],[25],[31],[26],[30] ]
y = [77,62,93,84,59,64,80,75,58,91,51,73,65,84]
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
regr.fit(x,y)
pred = regr.predict([[40],[5],[15]])
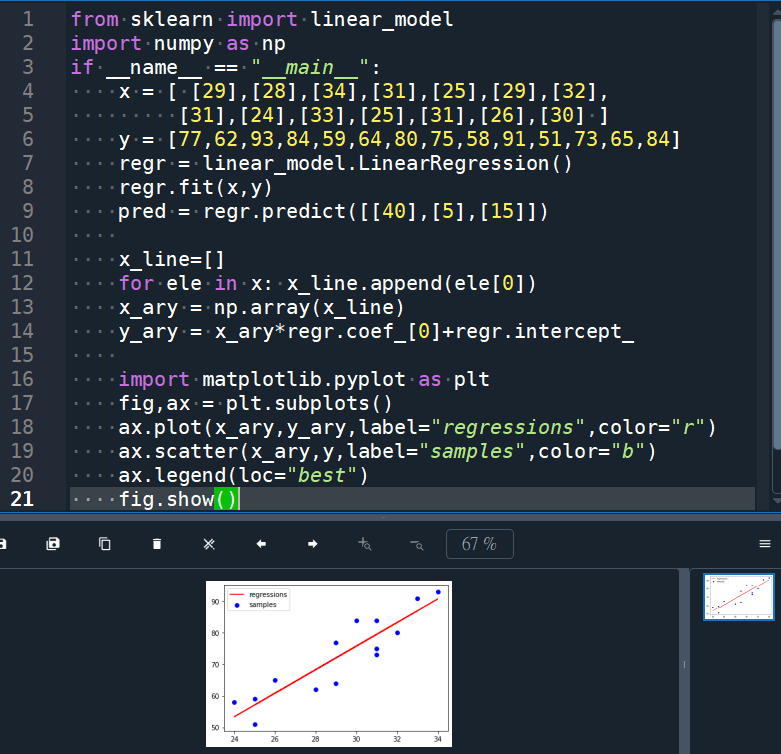
加碼題:

from sklearn import linear_model
import numpy as np
if __name__ == “__main__”:
x = [ [29],[28],[34],[31],[25],[29],[32],
[31],[24],[33],[25],[31],[26],[30] ]
y = [77,62,93,84,59,64,80,75,58,91,51,73,65,84]
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
regr.fit(x,y)
pred = regr.predict([[40],[5],[15]])
x_line=[]
for ele in x: x_line.append(ele[0])
x_ary = np.array(x_line)
y_ary = x_ary*regr.coef_[0]+regr.intercept_
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x_ary,y_ary,label=”regressions”,color=”r”)
ax.scatter(x_ary,y,label=”samples”,color=”b”)
ax.legend(loc=”best”)
fig.show()
參考解答:


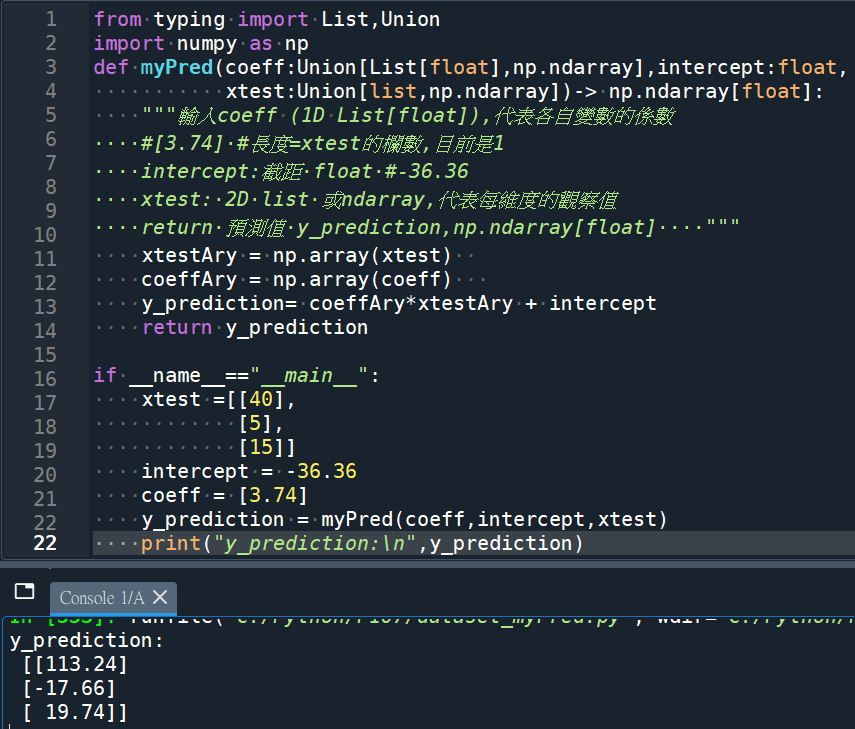
from typing import List,Union
import numpy as np
def myPred(coeff:Union[List[float],np.ndarray],intercept:float,
xtest:Union[list,np.ndarray])-> np.ndarray[float]:
“””輸入coeff (1D List[float]),代表各自變數的係數
#[3.74] #長度=xtest的欄數(.shape[1]),目前是1
intercept:截距 float #-36.36
xtest: 2D list 或ndarray,代表每維度的觀察值
return 預測值 y_prediction,np.ndarray[float] “””
xtestAry = np.array(xtest)
coeffAry = np.array(coeff)
y_prediction= coeffAry*xtestAry + intercept
return y_prediction
if __name__==”__main__”:
xtest =[[40],
[5],
[15]]
intercept = -36.36
coeff = [3.74]
y_prediction = myPred(coeff,intercept,xtest)
print(“y_prediction:\n”,y_prediction)
#y_prediction 不該是2D
#應該是因為xtest的第二維長度只有1
#幸運跑出來而已,還要繼續處理的
#coeff[0]*xtest的第0欄+coeff[1]*xtest的第1欄+…
#需要取直欄,pandas可能比較好用
#或使用array的切片方式
參考解答:

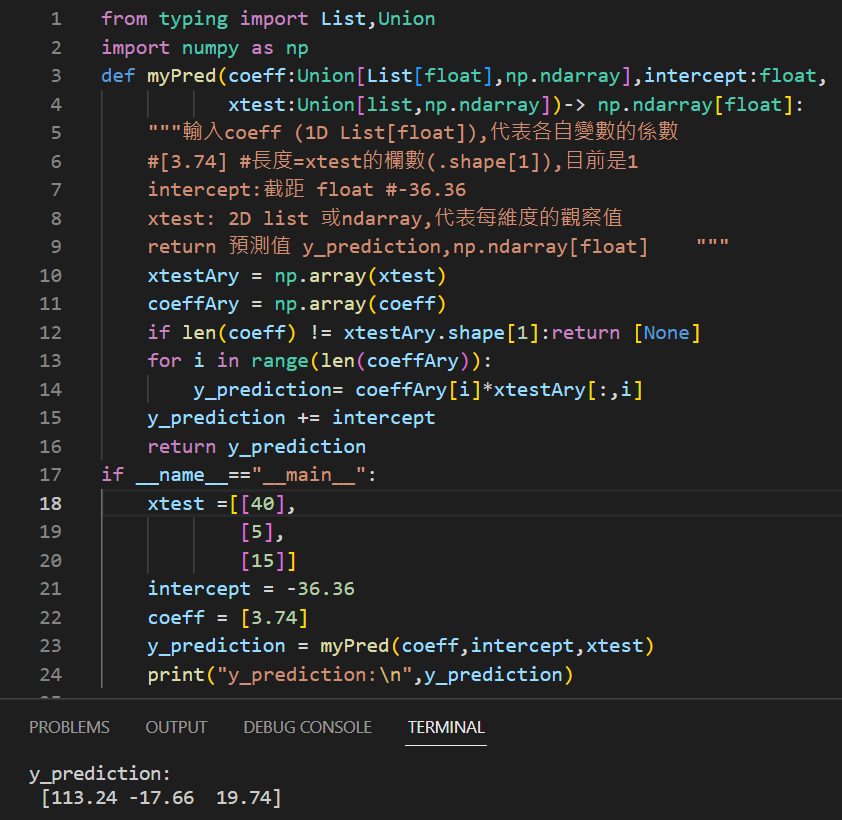
小修正:
from typing import List,Union
import numpy as np
def myPred(coeff:Union[List[float],np.ndarray],intercept:float,
xtest:Union[list,np.ndarray])-> np.ndarray[float]:
“””輸入coeff (1D List[float]),代表各自變數的係數
#[3.74] #長度=xtest的欄數(.shape[1]),目前是1
intercept:截距 float #-36.36
xtest: 2D list 或ndarray,代表每維度的觀察值
return 預測值 y_prediction,np.ndarray[float] “””
xtestAry = np.array(xtest)
coeffAry = np.array(coeff)
if len(coeff) != xtestAry.shape[1]:return [None]
for i in range(len(coeffAry)):
y_prediction= coeffAry[i]*xtestAry[:,i] #+intercept?
y_prediction += intercept
#+intercept放迴圈內可能會重複加
#本例迴圈僅有一次,所以看不出差別
return y_prediction
if __name__==”__main__”:
xtest =[[40],
[5],
[15]]
intercept = -36.36
coeff = [3.74]
y_prediction = myPred(coeff,intercept,xtest)
print(“y_prediction:\n”,y_prediction)
![Python: 字串 str.find(關鍵字[,start][,end]),找不到的話回傳-1,如何找出資料字串中,所有關鍵字的index?詞頻計算 Python: 字串 str.find(關鍵字[,start][,end]),找不到的話回傳-1,如何找出資料字串中,所有關鍵字的index?詞頻計算](https://i1.wp.com/savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/20221122100657_32.png?quality=90&zoom=2&ssl=1&resize=350%2C233)








![Python: List[ pandas.Series ] 轉DataFrame技巧:正確理解row和column的關係,同 concat( List[ pandas.Series ], axis=1 ).T - 儲蓄保險王](https://savingking.com.tw/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/20250422150133_0_1cfa94-513x245.png)
近期留言